|
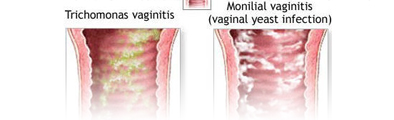
Vaginitis
Vaginitis can be described as an inflammation of the vagina and vulva. It is a fairly common problem with women. This can be avoided by taking proper treatment in the initial stages itself. But women usually tend to hide this problem.
Changes in the activity of the vaginal epithelium and in the vaginal secretion at different ages have a profound influence on the defense against vaginal infection. In the adult, the normal vaginal moisture or secretion consists of mucous and discarded vaginal cells. This discharge generally causes no irritation though the amount secreted and consistency vary. The variance is also due to the periodicity of the menstrual cycle and psychological conditions. Normal healthy women do not suffer from the sensations of the itching, burning, pain or irritation.
In unhealthy women and in abnormal conditions, the resident organisms (bacteria) multiply rapidly and produce excessive waste products. It causes tissue irritation in this region leading to itching, swelling, and burning. There is increase in the frequency or discharge of urine which is accompanied with an unpleasant order.
Symptoms
The symptoms of vaginitis are feeling of heat and fullness in the vagina, a dragging feeling in the groin, increased urinary frequency and vaginal discharge, that is, leucorrhoea. The clear or white secretion becomes purulent and yellow. The severity of leucorrhoea depends upon the degree of bacterial infection.
Causes
The main causes of vaginitis are irritation of vagina by external factors like cuts, abrasions in this region, constant wearing of tight-fitting clothes and wearing unclean clothes, using dirty or infected water and lack of hygiene.
Certain medications and treatments can increase susceptibility to infection. These include the use of antibiotics, hormones and excessive douching. Susceptibility is greater in cases of pregnancy, diabetes and certain psychological conditions as well as during the later half of the menstrual cycle. Irritation from contraceptive devices can also lead to this condition. Unhygienic conditions combined with wrong dietary habits increase toxemia thereby lowering body resistance.
According to the nature cure philosophy, whenever the body is loaded with toxins or morbid matter, it tried to eliminate it through the eliminative organs. In women, this elimination is established in the form of profused discharge, that is leucorrhoea, initially, in later stages, the discharge can become offensive in cases of chronic inflammation.
|
|