|
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is one of the most stubborn skin diseases. It is a chronic disease characterized by thick, red, silvery, scaled patches of skin. This disease affects both sexes equally and usually first appears at the age ranging from 15 to 30 years, although it may appear at any age. It is, however, rare in infancy and old age. Psoriasis is not contagious.
Symptoms
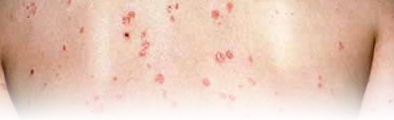
Generally, the skin of the person suffering from psoriasis appears red and irritated and may be covered with bright silvery scales. Sometimes there is also a little itching. Areas usually involved are elbows, knees, the skin behind the ears, trunk and scalp. The disease may also affect the underarm and genital areas. The lesions vary in size from minute papules only just visible, to sheets covering large parts of the body. Quite often, they are discs from 1.5 cm. to several centimeters in size. The lesions of psoriasis are always dry and rarely become infected.
Causes
The modern medical system has not been able to establish the exact cause of psoriasis. Recent studies have shown that psoriasis involves an abnormality in the mechanism in which the skin grows and replaces itself. This abnormality is related to the metabolism of amino-acids, the protein chemicals which are nature’s basic building blocks for the reproduction of cell tissues. Heredity also plays a role in the development of psoriasis as it tends to occur in families. About 30 per cent of the patients have a family history of the disease.
The factors that aggravate and precipitate the outbreak of psoriasis are injury to the skin in the form of cuts, burns, minor abrasions, changes in the seasons, physical and emotional stress, infections and use of certain medicines for the treatment of other diseases.
Treatment
Since psoriasis is a metabolic disease, a cleansing juice fast for about seven days is always desirable in the beginning of the treatment. Carrots, beats, cucumbers and grapes may be used for juices. Juices of citrus fruits should be avoided. The warm water enema should be used daily to cleanse the bowels during the fast. After the juice fast, the patient should adopt the diet of three basic food groups, namely (i) seeds, nuts and grains, (ii) vegetables and (iii) fruits, with emphasis on raw seeds and nuts, especially seasame seeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds and plenty of organically grown raw vegetables and fruits.
|
|